Advancement in Nanotechnology: Small Size, Big Impact
The field of nanotechnology has witnessed unprecedented growth and innovation. Nano-technology, often referred to as the science of the small, deals with structures and materials at the nanoscale, typically ranging from 1 to 100 nanometers. This remarkable field has opened up new avenues across various industries, from medicine to electronics, offering countless possibilities for enhancing our daily lives. In this article, we will delve into the exciting world of nanotechnology, exploring how these tiny wonders are making a colossal impact.
mic and molecular scale. It’s a multidisciplinary field that combines principles of physics, chemistry, biology, and engineering to create, understand, and utilize structures and devices at the nanoscale.
The Nanoscale World
At the nanoscale, materials often exhibit unique properties that differ from their bulk counterparts. These properties can include enhanced strength, improved conductivity, and altered optical characteristics. Researchers have harnessed these properties to develop groundbreaking technologies.
Applications in Medicine
Drug Delivery
One of the most promising applications of nano-technology in medicine is drug delivery. Nanoscale carriers can transport drugs directly to target cells, increasing drug efficacy while minimizing side effects.
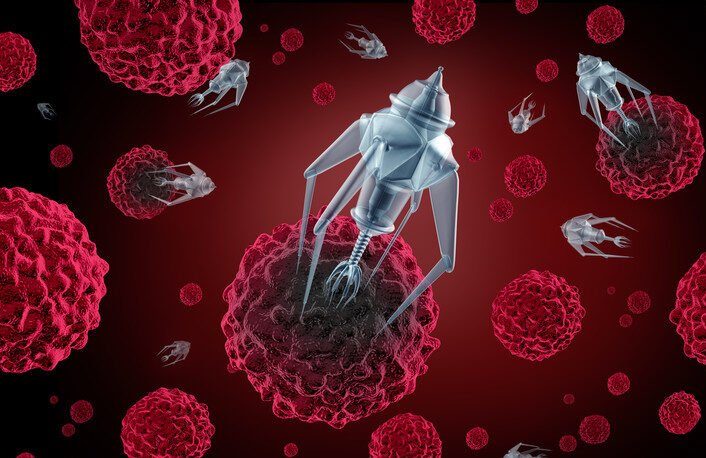
Cancer Treatmen
Nanoparticles can be engineered to target and destroy cancer cells selectively. This approach holds great promise for improving cancer treatment outcomes.
Nanotechnology in Electronics
Miniaturization
Nano-technology has enabled the continued miniaturization of electronic components, leading to smaller and more powerful devices such as smartphones and laptops.
Improved Performance
By harnessing the unique properties of nanomaterials, electronic devices can achieve higher performance levels, contributing to faster processors and longer-lasting batteries.
Environmental Benefits
Nano-technology also offers eco-friendly solutions, such as efficient water purification and advanced materials that reduce energy consumption.
Challenges and Ethical Considerations
While nanotechnology offers remarkable benefits, it also raises concerns regarding safety, privacy, and the potential misuse of advanced materials. Ethical considerations are paramount as this field continues to evolve.
Nanotechnology, the science of manipulating matter at the nanoscale, has made remarkable strides in recent years. With applications ranging from medicine and electronics to energy and materials science, nanotechnology promises groundbreaking innovations. However, as we delve deeper into the world of nanoscale materials and devices, a host of challenges and ethical considerations emerge. In this article, we will explore the multifaceted landscape of nanotechnology, examining both the incredible potential it holds and the complex issues it raises.
The Nanoscale Revolution
Understanding Nano-technology
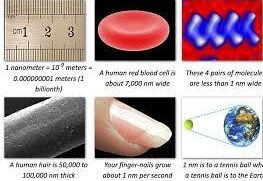
Nanotechnology involves working with materials at the nanoscale, typically in the range of 1 to 100 nanometers. At this scale, matter exhibits unique properties, enabling novel applications.
Nanomedicine
Nanotechnology is revolutionizing healthcare by allowing precise drug delivery, early disease detection, and targeted therapy.
Nanoelectronics
Nanoelectronic devices promise faster, smaller, and more energy-efficient electronics, paving the way for the future of computing.
Challenges in Nanotechnology
Safety Concerns
Working with nanomaterials can pose health and environmental risks, necessitating stringent safety protocols.
Regulatory Framework
Establishing regulations for nanotechnology is challenging due to its rapid development and diverse applications.
Cost and Accessibility
Nano-technology innovations may be expensive, limiting their accessibility to certain populations.
Ethical Considerations
Privacy and Surveillance
Nanoscale sensors and devices raise concerns about privacy invasion and surveillance capabilities.
Dual-Use Dilemma
Nanotechnology can be used for both benevolent and malevolent purposes, necessitating ethical considerations.
Environmental Impact
The disposal and potential toxicity of nanomaterials raise concerns about their long-term environmental effects.
Bridging the Gap
Interdisciplinary Collaboration
Addressing nano-technology challenges and ethics requires collaboration among scientists, ethicists, policymakers, and more.
Public Engagement
Educating the public about nanotechnology’s potential and risks is vital for informed decision-making.
Ethical Frameworks
Developing ethical frameworks can guide the responsible development and deployment of nanotechnology.
Future Prospects
The future of nano-technology holds immense promise. Researchers are exploring nanomedicine, nanoelectronics, and nanomaterials with the potential to revolutionize various industries.
Conclusion
In conclusion, nanotechnology’s impact on our world cannot be overstated. From healthcare to electronics and environmental sustainability, the small size of nanomaterials has indeed brought about a big impact. As we navigate the exciting frontier of nanotechnology, it’s essential to strike a balance between innovation and ethical responsibility.
Read More: 5G Technology: Unlocking the Potential of Hyperconnectivity
FAQs
What is nano-technology?
Nanotechnology is the science and engineering of materials at the nanoscale, typically between 1 and 100 nanometers in size.
How does nano-technology impact medicine?
Nanotechnology has revolutionized medicine by enabling precise drug delivery, targeted cancer treatments, and advanced diagnostic techniques.
Is nano-technology safe for the environment?
While nanotechnology offers environmental benefits, there are concerns about the potential environmental impact of nanomaterials. Research is ongoing to ensure their safety.
What are the ethical concerns surrounding nano-technology?
Ethical concerns include privacy issues, the responsible use of advanced materials, and potential misuse for harmful purposes.
What can we expect from nano-technology in the future?
The future of nanotechnology holds promise in various fields, including healthcare, electronics, and sustainability. Expect more innovations and breakthroughs in the coming years.
Read More: Autonomous Vehicles: Towards a Driverless Future